Biogas plant
Contents
ToggleBiogas plant: An ecological solution for energy production
Introduction
In determining the lifetime of the environment and climate change, they are among the fundamental challenges facing humanity. That is why it is so important to look for alternative, ecological energy sources. One such technology is a biogas plant that can turn to energy generation. In this article we will look at biogas plants, their additional benefits that can occur.
What is a biogas plant?
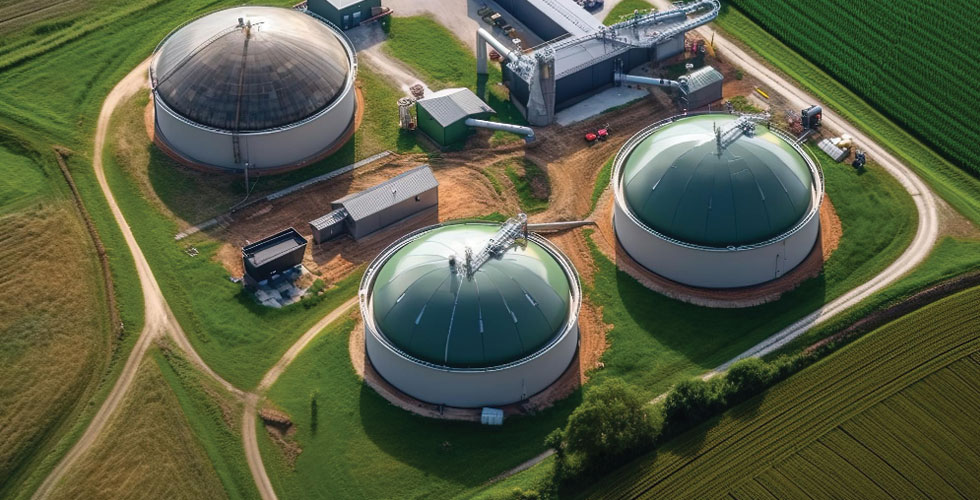
A biogas plant is an installation where biogas is produced from biomass, i.e. organic substances such as plant residues, manure, cut grass or agricultural residues. This process is called anaerobic digestion and takes place in special tanks called fermentors.
Anaerobic digestion consists in the decomposition of organic substances by microorganisms under anaerobic conditions. This process produces biogas, which consists mainly of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Biogas can be used as fuel for the production of electricity and heat.
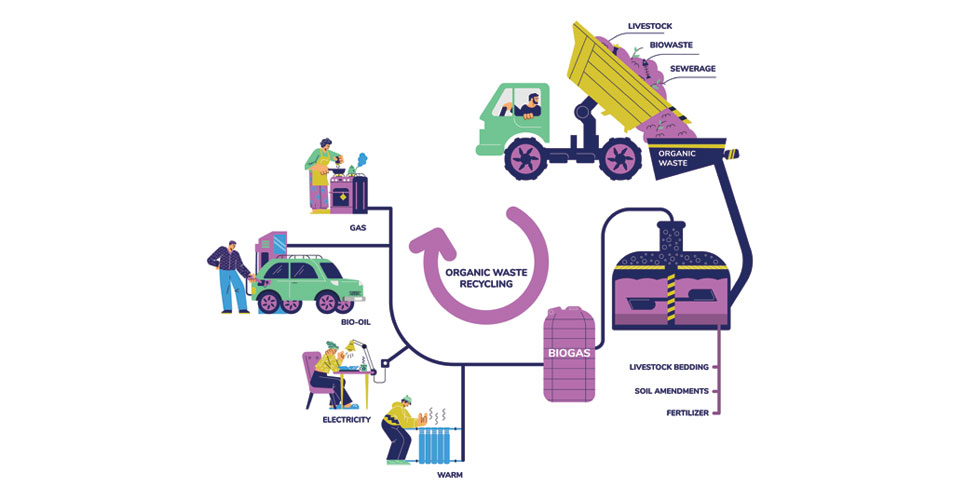
How does a biogas plant work?
A biogas plant consists of several main components. First, organic raw materials are processed in fermenters, where anaerobic fermentation takes place. Micro-organisms in the presence of heat and moisture break down the organic matter, releasing biogas.
The biogas is then collected and treated to remove unwanted impurities such as hydrogen sulphide or ammonia. The clean biogas can then be stored or used for energy production.
In the case of electricity production, the biogas is combusted in an internal combustion engine or turbo-gas plant, which drives an electric generator. The result is electricity that can be used in households, industrial plants or connected to the electricity grid.
On the other hand, if the aim is to produce heat, biogas can be burned in a boiler or used in cogeneration, where heat and electricity are generated simultaneously.
Benefits of biogas plants
Biogas plants have many benefits, both for the environment and for the economy.
- Ecological energy source: Biogas plants contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Biogas resulting from anaerobic digestion is a renewable energy source, and the combustion of biogas is much less harmful to the environment than the combustion of fossil fuels.
- Waste recycling: Biogas plants make it possible to process and recycle various types of organic waste that might otherwise end up in landfills and contribute to environmental pollution.
- Organic fertiliser production: The anaerobic fermentation process in biogas plants leads to the production of digestate, which is a valuable organic fertiliser. Digestate can be used to fertilise fields, which contributes to improving soil quality.
- Availability of raw materials: Organic feedstocks used in biogas plants, such as manure or crop residues, are widely available in rural agricultural areas. The use of these raw materials for energy production provides farmers with an additional source of income.
Summary
Biogas plants provide an environmentally friendly solution for the production of electricity and heat. Through anaerobic digestion, biogas is produced from organic raw materials such as plant residues or manure. The benefits of biogas plants are numerous - from reducing greenhouse gas emissions and recycling waste, to producing organic fertiliser and providing farmers with an additional source of income.
In an era of increasing energy demand and the fight against climate change, biogas plants are a promising solution. Investment in the development of biogas plants should be supported by both public and private institutions so that we can enjoy clean energy and a sustainable environment.